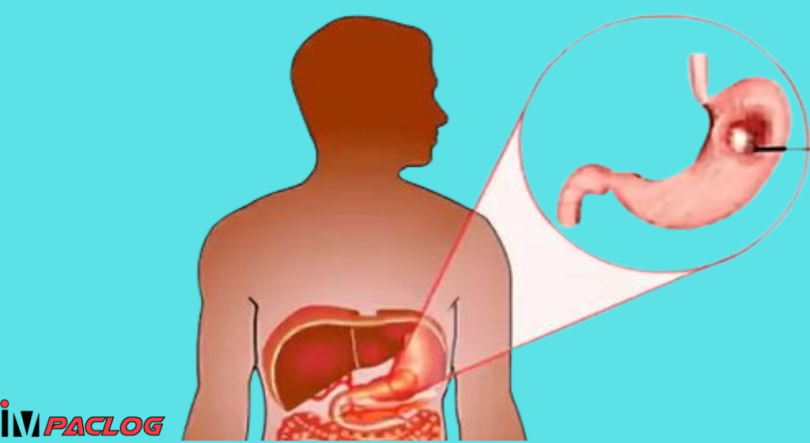
Gastric cancer is one of the malignant tumors that affect the stomach. Today, the Western world is witnessing a decline in the incidence of stomach cancer. Stomach cancer is divided into two types: the first affects the upper part of the stomach and the second affects the lower part of the stomach.
The rates of infection with the first type, which affects the upper part of the stomach, are higher than the rates of the other type. In developing countries, stomach cancer ranks third in terms of prevalence among various cancer diseases.
A distinction is usually made between the different stages of development of stomach cancer, because the infection at an early stage is limited to the area of the inner membrane of the stomach, that is, the gastric mucosa, and surgical treatment at this stage is often very effective. With excellent results.
But if the injury extends beyond the lining of the stomach to the muscle layer or lymph nodes surrounding the stomach, the chances of recovery are greatly reduced, and if the injury is in the upper part of the stomach, the chances of recovery are reduced. . Only if the injury is in the lower part of the stomach.
Symptoms of stomach cancer
Stomach cancer in its early stages causes no symptoms or signs, making it difficult to diagnose. Symptoms of stomach cancer include:
Feeling tense and uncomfortable.
Pain in the upper abdomen.
Bloating or vomiting after eating.
Lack of appetite.
And weight loss.
Feeling weak due to anemia.
Black stool.
The presence of blood in the vomit.
Peptic ulcer disease can sometimes cause symptoms similar to stomach cancer.
Causes and risk factors of stomach cancer
Below are the main causes of stomach cancer
1- Infection caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria
Causes of stomach cancer One of the most important factors that increase the risk of stomach cancer is exposure to a bacteria known as Helicobacter pylori, which causes inflammation of the inner lining of the stomach.
About a third of stomach cancer cases are primarily due to exposure to infection with these bacteria, but despite this, most people who carry these bacteria do not develop any of the diseases that affect the stomach.
2- Diet
Eating smoked, dried, or salted foods, or foods that contain spices, increases the amount of nitrates in the stomach, and these substances inside the stomach undergo chemical changes that turn them into carcinogenic substances.
On the other hand, eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, or safely stored and refrigerated foods reduces the risk of stomach cancer.
- Other reasons
In addition to these two factors, smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages are reasons that increase the risk of upper stomach cancer. The possibility of developing stomach cancer also increases during stomach surgery, but this risk factor becomes serious after twenty years of life. Date of operation.
Statistics indicate that the probability of developing stomach cancer increases by at least two to four times among people whose relatives have had stomach cancer, and it is more common among men than among women. Stomach cancer appears especially in the age group between 70 and 75 years.
Complications of stomach cancer
If stomach cancer develops to an advanced stage, it can cause many complications such as:
Gastrointestinal bleeding.
Stomach perforation.
Small intestine obstruction.
Diagnosis of stomach cancer
There are different methods for diagnosing stomach cancer, the most important of which are:
1- Gastroscopy
Stomach cancer is often diagnosed by gastroscopy, a test to detect a stomach ulcer, tumor mass, or thickening of the inner lining of the stomach. During the examination, a small sample, i.e. a biopsy, may be taken for microscopic examination.
2- Barium injection radiography.
It is no longer the preferred method for diagnosing stomach cancer, and the imaging method is becoming less acceptable and reliable day after day.
3- Computed tomography (CT)
It can detect whether the cancer has spread beyond the stomach wall or whether the inner wall of the stomach has become thickened, and this method is usually used to complete the medical clarification process.
- Endoscopic ultrasound – EUS
This test can detect how far the cancer has penetrated the stomach wall and lymph nodes.
Stomach cancer treatment
Treatment for stomach cancer depends on the stage at which stomach cancer is diagnosed. Surgery to remove a stomach tumor (gastrectomy) is the only method of stomach cancer treatment that completely cures stomach cancer.
During this operation, part of the stomach may be removed or the entire stomach may be removed depending on the needs of the tumor and the extent of its spread. In some special cases, especially those in which the tumor has spread to the stomach wall, a combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy is generally recommended.
In cases where stomach cancer is discovered at an advanced stage, treatment generally focuses on supporting the patient, in terms of maintaining a healthy diet and palliative treatments.
Sometimes it may be necessary to feed the patient through a special opening in the abdominal wall that leads directly into the stomach, called a gastrostomy. The patient can sometimes be fed through an opening made in the intestine, called a jejunostomy.
However, people whose close relatives have had stomach cancer are advised to be tested for Helicobacter pylori and treated if necessary.
Preventing stomach cancer
Stomach cancer can be prevented through the following measures:
Limit the amount of alcohol you drink and do not use tobacco products.
Avoid eating smoked and spicy foods, as well as salty meat and fish.
Eat fresh fruits and vegetables and plenty of whole-grain foods, such as whole-grain breads, cereals, pasta and rice.
Maintain a healthy weight.